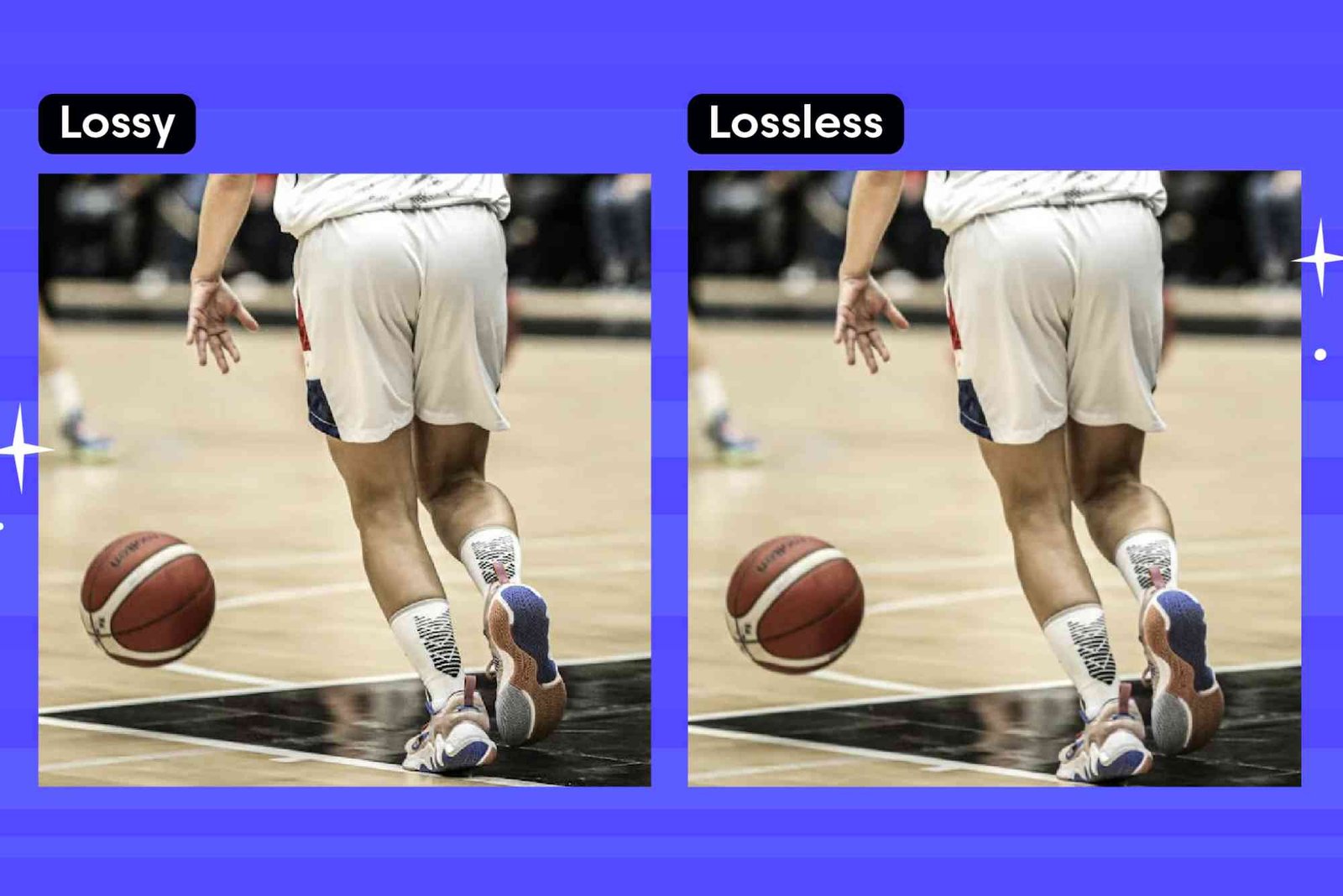
What is Compression
Compression is a technique used to reduce the file size of digital media, making storage and transmission more efficient. It plays a crucial role in digital data management, affecting everything from images and audio to videos and documents. There are two main types of compression: lossy and lossless. Understanding their differences is essential for choosing the right method based on quality, file size, and usage.
Lossy vs. Lossless Compression: The Key Differences
Lossy compression reduces file size by permanently removing some data, resulting in a loss of quality. It is commonly used for images (JPEG), audio (MP3), and video (MP4). On the other hand, lossless compression maintains all original data, allowing files to be restored to their original form without quality degradation. This method is typically used for text files, PNG images, and FLAC audio.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Lossy Compression | Lossless Compression |
|---|---|---|
| Quality | Reduced | Maintained |
| File Size | Smaller | Larger |
| Reversibility | Irreversible | Reversible |
| Use Cases | Images, Audio, Video | Documents, PNG, FLAC |
How Lossy Compression Works
Lossy compression removes redundant or less important data to achieve smaller file sizes. For instance, an Image Compressor like Image Compressor eliminates minor color variations to reduce image size while maintaining acceptable quality. However, excessive compression can result in visible quality loss, known as compression artifacts.
Step-by-Step Process
- Analyzing the file: The algorithm identifies redundant data.
- Applying compression: Less noticeable details are discarded.
- Encoding: The file is saved in a new, smaller format (e.g., JPEG, MP3).
- Retrieval: The compressed file is used, but it cannot be fully restored to its original form.
How Lossless Compression Works
Lossless compression preserves all data, making it ideal for scenarios where quality retention is critical. It works by encoding data more efficiently rather than removing it.
Step-by-Step Process
- Identifying patterns: The algorithm detects repetitive data.
- Encoding: It replaces redundant sequences with shorter representations.
- Storing the compressed file: The entire file structure remains intact.
- Decompression: The file can be fully restored without loss of data.
When to Use Lossy or Lossless Compression
The choice between lossy and lossless compression depends on the application:
- Use lossy compression for web images, streaming music, and videos where small file sizes are more critical than perfect quality.
- Use lossless compression for professional photography, audio mastering, and document storage where quality is paramount.
FAQs
1. Which is better: Lossy or Lossless Compression?
It depends on your needs. Lossy is better for saving space, while lossless is best for maintaining original quality.
2. Can you convert lossy files back to their original quality?
No, once data is lost through lossy compression, it cannot be recovered.
3. What are common formats for each type?
Lossy: JPEG, MP3, MP4; Lossless: PNG, FLAC, ZIP.
4. Where can I find professional compression tools?
For high-quality image compression, visit Digital Ranker Dubai.
5. Where is Digital Ranker Dubai located?
Find us at Digital Ranker Dubai Location.